7 Surprising Tips for Bigger Arms: Unlock Your Full Potential
Introduction
Achieving bigger, stronger arms is a common goal for many fitness enthusiasts and athletes. While traditional exercises like bicep curls and tricep pushdowns are staples in most routines, they might not be enough to maximize your arm growth. This comprehensive guide reveals seven surprising tips that can transform your arm training and help you break through plateaus. By integrating these strategies into your workout regimen, you can accelerate muscle development and attain the impressive arm size you’ve always desired.
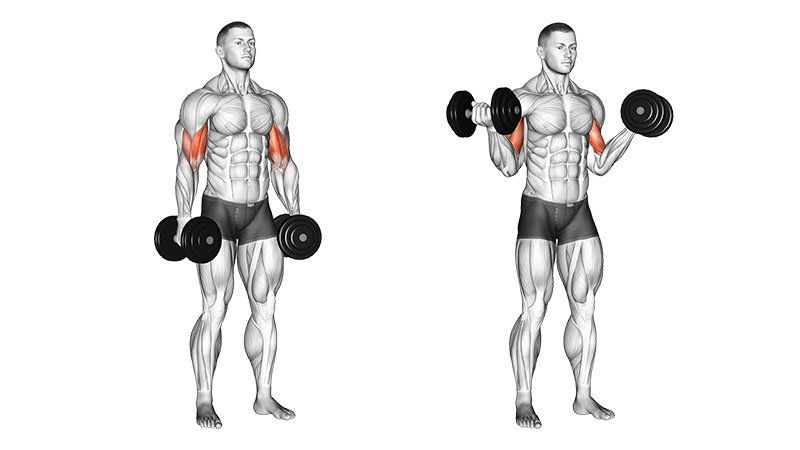
1. Prioritize Triceps: The Unsung Hero of Arm Size
Understanding the Role of Triceps
The triceps brachii muscle makes up approximately two-thirds of your upper arm’s muscle mass. Despite this, many people focus predominantly on bicep exercises, overlooking the significant potential for growth in the triceps. The triceps consist of three heads—the long, lateral, and medial—which, when fully developed, contribute substantially to overall arm size.
Effective Triceps Exercises
- Close-Grip Bench Press: This compound movement emphasizes the triceps while also engaging the chest and shoulders. Using a narrower grip shifts the focus to the triceps, promoting strength and mass gains.
- Parallel Bar Dips: Dips are excellent for building triceps mass. Keeping your torso upright targets the triceps more effectively, while leaning forward shifts emphasis to the chest.
- Overhead Triceps Extensions: Performing this exercise stretches the long head of the triceps, stimulating muscle fibers that are not fully engaged during other movements. Use dumbbells, cables, or an EZ-bar for variation.
Training Tips
- Exercise Order: Start your workouts with compound triceps exercises when energy levels are highest.
- Rep Ranges: Incorporate both heavy weights with lower reps (6–8) and lighter weights with higher reps (10–15) to target different muscle fibers.
- Mind-Muscle Connection: Focus on feeling the triceps work during each exercise to enhance muscle activation.
2. Embrace Compound Movements for Holistic Growth
The Power of Multi-Joint Exercises
Compound exercises engage multiple joints and muscle groups simultaneously, leading to greater overall strength and muscle development. Incorporating these movements into your routine not only targets the arms but also stimulates the release of anabolic hormones like testosterone and growth hormone, which facilitate muscle growth throughout the body.
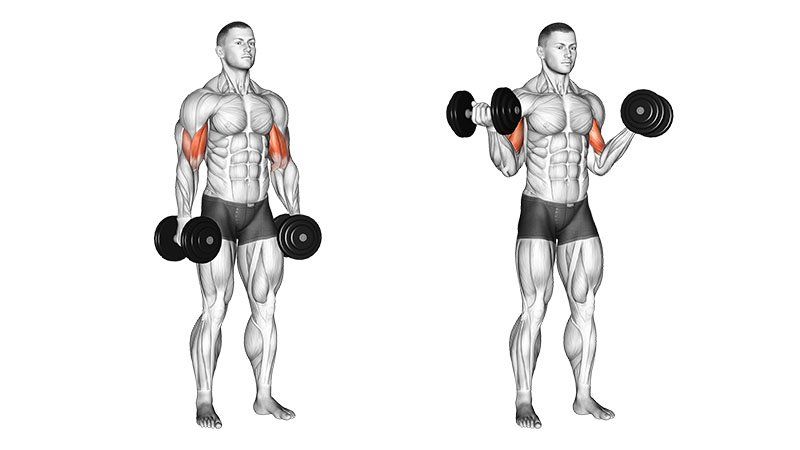
Key Compound Exercises
- Pull-Ups and Chin-Ups: These exercises work the biceps, forearms, back, and shoulders. Varying your grip width and orientation (underhand or overhand) can shift the emphasis between muscle groups.
- Bench Press Variations: Including flat, incline, and decline bench presses engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps from different angles.
- Rows (Barbell, Dumbbell, Cable): Rows target the back and biceps, promoting balanced upper body development.
Hormonal Benefits
- Increased Testosterone: Heavy compound lifts stimulate testosterone production, enhancing muscle protein synthesis.
- Growth Hormone Release: High-intensity compound movements elevate growth hormone levels, aiding in muscle repair and growth.
3. Strengthen Your Forearms for Enhanced Performance
The Importance of Grip Strength
A strong grip is essential for lifting heavier weights and performing exercises with proper form. Weak forearms can limit your ability to fully engage arm muscles during workouts, hindering overall development.
Forearm-Focused Exercises
- Wrist Curls and Reverse Wrist Curls: Target the flexor and extensor muscles of the forearm to build size and strength.
- Farmer’s Walks: Holding heavy weights while walking improves grip strength and forearm endurance. This functional exercise also engages the core and stabilizer muscles.
- Plate Pinches: Pinching weight plates together and holding them for time strengthens the forearms and enhances grip.
Integrating Grip Training
- Thick-Grip Equipment: Use fat grips or thick bars to increase the demand on your forearms during standard lifts.
- Avoid Overuse of Straps: While lifting straps can help with heavier weights, relying on them too much can impede forearm development.
4. Implement Progressive Overload Strategically
The Principle of Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is the gradual increase of stress placed upon the body during exercise training. This principle is fundamental for achieving continual gains in muscle size and strength.
Methods of Progressive Overload
- Increase Weight: Gradually add more weight to your lifts as your strength improves.
- Increase Volume: Add more sets or repetitions to your exercises.
- Reduce Rest Periods: Shorter rest intervals can increase workout intensity and metabolic stress.
- Enhance Exercise Form: Improving technique can make exercises more challenging and effective.
Tracking Progress
- Training Logs: Keep detailed records of your workouts, including exercises, weights, reps, and rest periods.
- Regular Assessments: Periodically test your one-rep max (1RM) or rep maxes to gauge strength improvements.
5. Diversify Your Grip and Exercise Angles
Targeting Different Muscle Fibers
Altering your grip and the angles at which you perform exercises can activate different muscle fibers within your arms, promoting more comprehensive development.
Grip Variations
- Supinated Grip (Underhand): Emphasizes the biceps brachii, particularly during exercises like barbell curls and underhand pull-ups.
- Pronated Grip (Overhand): Targets the brachialis and brachioradialis muscles, which can add width to the upper arm.
- Neutral Grip (Hammer): Engages both the biceps and forearm muscles, providing balanced development.
Angle Variations
- Incline Curls: Performing curls on an incline bench stretches the biceps and targets the long head.
- Preacher Curls: Focuses on the short head of the biceps and reduces cheating by stabilizing the arms.
- Overhead Triceps Extensions: Engages the long head of the triceps more effectively than other triceps exercises.
Exercise Selection
- Rotational Programming: Change exercises every 4–6 weeks to prevent adaptation and encourage continuous growth.
- Unilateral Training: Incorporate single-arm movements to address muscle imbalances and improve symmetry.
6. Use Advanced Training Techniques: Supersets and Drop Sets
Maximizing Muscle Fatigue
Advanced training techniques like supersets and drop sets can intensify your workouts by increasing time under tension and metabolic stress, key factors in muscle hypertrophy.
Supersets
- Antagonist Supersets: Pair exercises for opposing muscle groups (e.g., bicep curls followed by tricep pushdowns) to enhance efficiency and recovery.
- Same Muscle Group Supersets: Perform two exercises targeting the same muscle group back-to-back (e.g., hammer curls and concentration curls) to fully fatigue the muscles.
Drop Sets
- Technique: After reaching failure with a certain weight, immediately reduce the weight by 20–30% and continue the exercise until failure again.
- Application: Use drop sets on the last set of an exercise to maximize muscle exhaustion.
Benefits
- Increased Intensity: These techniques push muscles beyond their usual limits, promoting greater adaptation.
- Time-Efficient Workouts: Intensifying workouts can reduce total training time while maintaining effectiveness.
Caution
- Avoid Overtraining: Use advanced techniques sparingly to prevent excessive muscle damage and overtraining.
- Recovery: Ensure adequate rest and nutrition to support the increased demands on your body.
7. Optimize Nutrition and Recovery for Muscle Growth
The Role of Diet in Muscle Building
Proper nutrition is critical for muscle repair, growth, and overall performance. Without sufficient nutrients, your body cannot effectively build muscle, regardless of your training intensity.
Macronutrient Considerations
- Protein: Essential for muscle synthesis. Consume high-quality protein sources like lean meats, eggs, dairy, legumes, and protein supplements. Aim for 1.6–2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight daily.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy for workouts and replenish glycogen stores. Focus on complex carbs such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Fats: Necessary for hormone production and joint health. Include healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Hydration
- Importance: Adequate hydration supports nutrient transport, muscle function, and recovery.
- Guidelines: Drink water consistently throughout the day, especially before, during, and after workouts.
Recovery Strategies
- Sleep: Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night. Sleep is crucial for hormonal balance and muscle recovery.
- Active Recovery: Engage in light activities like walking, stretching, or yoga to promote blood flow and reduce muscle soreness.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can impede recovery. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress.
Supplementation
- Whey Protein: Convenient source of high-quality protein to support muscle repair.
- Creatine Monohydrate: Enhances strength and power output, aiding in muscle growth.
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): May reduce muscle soreness and support recovery.
Note: Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Conclusion
Building bigger arms requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond traditional exercises. By prioritizing triceps training, embracing compound movements, strengthening your forearms, strategically implementing progressive overload, diversifying your grips and angles, utilizing advanced training techniques, and optimizing nutrition and recovery, you can accelerate your arm development.
Consistency and patience are essential. Muscle growth is a gradual process, and results come with sustained effort over time. Stay dedicated to your training regimen, listen to your body’s signals, and make adjustments as needed. With these surprising tips integrated into your routine, you’re well on your way to achieving impressive arm size and strength.
Sample Arm Workout Plan
Day 1: Triceps Emphasis
- Close-Grip Bench Press: 4 sets x 6 reps
- Overhead Triceps Extension: 3 sets x 10 reps
- Triceps Dips: 3 sets x 8 reps
- Rope Pushdowns (Drop Set): 3 sets x 12 reps; reduce weight by 20% after reaching failure
Day 2: Biceps and Forearms
- Chin-Ups: 4 sets x 8 reps
- Incline Dumbbell Curls: 3 sets x 10 reps
- Hammer Curls (Superset with Reverse Curls): 3 sets x 12 reps each
- Wrist Curls: 3 sets x 15 reps
Day 3: Compound Movements
- Pull-Ups (Vary Grip Each Set): 4 sets x 6 reps
- Barbell Rows: 4 sets x 8 reps
- Bench Press (Standard Grip): 4 sets x 6 reps
- Military Press: 3 sets x 8 reps
Note: Always begin workouts with a proper warm-up to prepare your muscles and reduce the risk of injury. Incorporate rest days to allow for muscle recovery.
Final Thoughts
Integrating these strategies into your fitness routine requires commitment and a willingness to push beyond your comfort zone. Remember to consult with a fitness professional if you’re new to weightlifting or have any underlying health conditions. With dedication and the right approach, bigger, stronger arms are within your reach.
Stay consistent, stay focused, and watch your arms transform.